
Cortisol levels are highest at the start of the working day, falling to the lowest levels in late evening with the onset of sleep. bound plus free) concentration of cortisol is measured for diagnostic purposes.įigure 9.1 The morphological zonation of the adrenal cortex, showing the three types of cells and their particular structural arrangement.ģ The diurnal rhythm of plasma This control mechanism is related to the rhythm of an individual’s sleeping-waking cycle ( Figure 9.3). The biologically active fraction of cortisol in plasma is the free (unbound) component, though usually the total (i.e. Changes in plasma occur in parallel to changes in. It is decreased in hypoproteinaemic states (e.g. Plasma is increased in pregnancy and with oestrogen treatment (e.g. In the circulation, glucocorticoids are mainly protein bound (~90%), chiefly to CBG (cortisol-binding globulin or transcortin). Glucocorticoids are also involved to some extent in regulating sodium and water homeostasis and the inflammatory and stress responses. Lipolysis is increased in adipose tissue, and proteolysis and amino acid release promoted in muscle. In the liver, cortisol stimulates gluconeogenesis, amino acid uptake and degradation, and ketogenesis. Glucocorticoids have widespread metabolic effects on carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism.
Sex steroid production also occurs in the adrenal cortex, mainly in the zona reticularis and to some extent in the zona fasciculata.
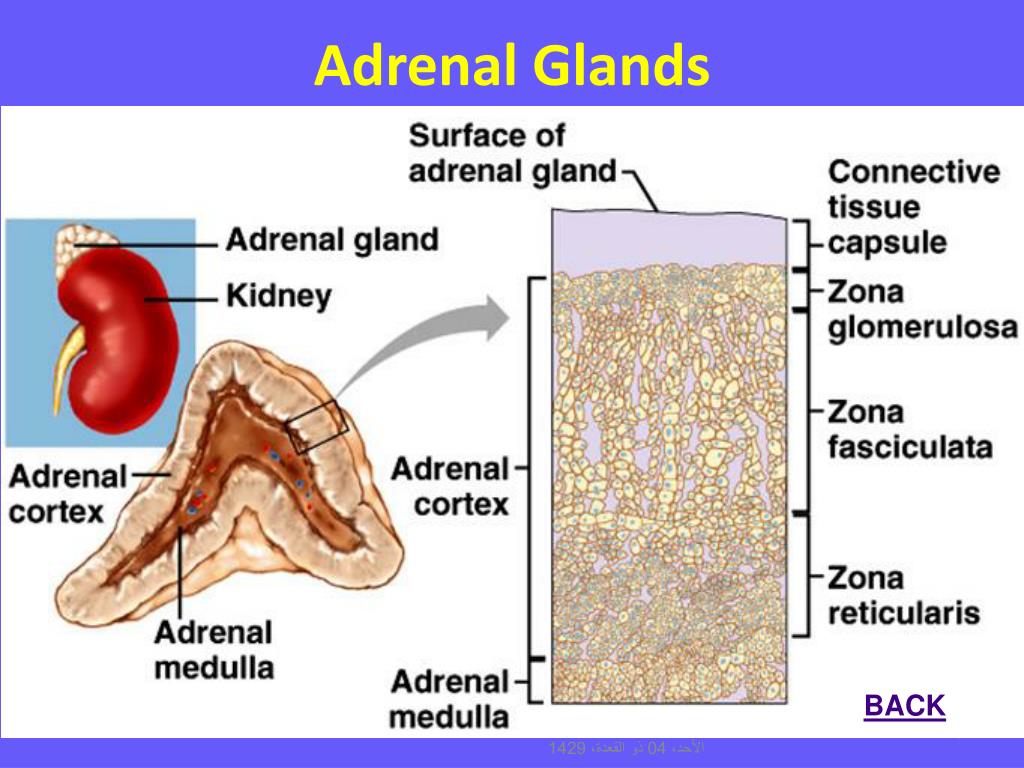
The deeper layers of the cortex, the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis, synthesise glucocorticoids, of which cortisol is the most important in man. The outermost zona glomerulosa is the site of synthesis of aldosterone, the principal mineralocorticoid. Three zones can be recognised in the adrenal cortex ( Figure 9.1). Regulation of adrenal steroid hormone synthesis and secretion


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
